In the year 1620, the Mayflower embarked on an arduous 64-day journey, navigating the vast Atlantic Ocean to transport the first Pilgrims from England to America. Centuries later, in 1919, aviators Alcock and Brown accomplished a monumental feat by completing the first non-stop transatlantic flight, soaring from Canada to Ireland in under 16 hours.
Fast forward to the present day, where an astonishing 4 million individuals annually embark on the popular route connecting New York and London, completing the voyage in a mere 7 hours. Over the past half-century, air travel has revolutionized accessibility, granting people from all walks of life the opportunity to explore the world, thanks to enhanced airline safety measures and the consequent reduction in ticket prices. Yet, as we look to the future, what groundbreaking advancement awaits the realm of air travel?
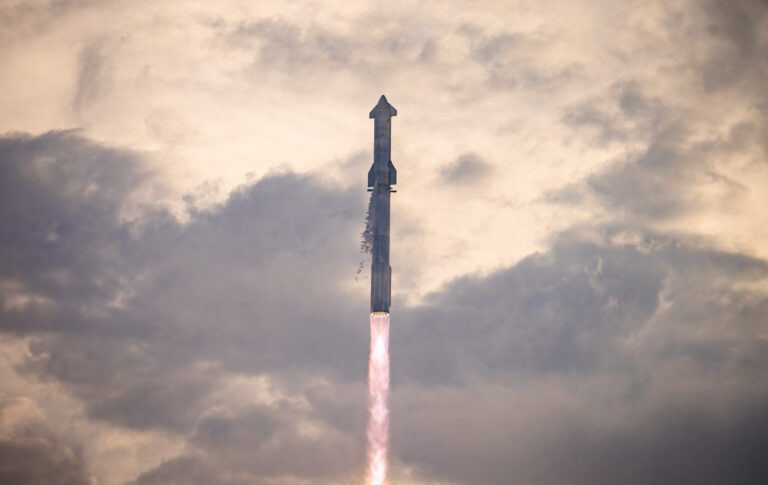
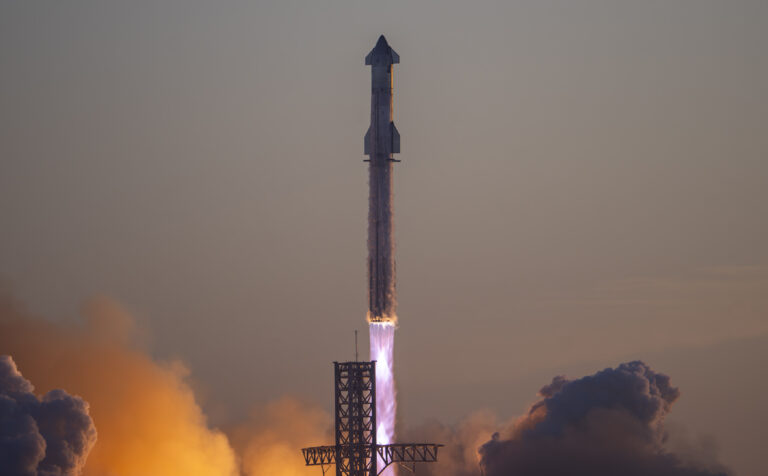
Starship’s Earth to Earth travel
In a paradigm-shifting announcement back in 2017, SpaceX boldly unveiled their ambitious vision to revolutionize Earth-to-Earth transportation through the utilization of their cutting-edge Starship spacecraft. Proposing a game-changing approach, SpaceX envisioned a seamless travel experience where passengers would embark on a vessel that transports them to a floating launch site. There, a fully equipped Starship would be poised to commence their rapid journey to their desired destination. Following launch, the Starship would gracefully separate from its booster and execute a precision-propulsive landing at its new arrival point.

By venturing beyond the Earth’s atmosphere, SpaceX’s Starship opens up the possibility of achieving unprecedented speeds, surpassing those of conventional airliners and leading to remarkable reductions in flight durations. The tantalizing prospect of reaching any destination on Earth in under an hour, with most international flights completed in a mind-boggling 30 minutes, is a vision that SpaceX confidently foresees.
As the construction of Starship progresses, fueled by SpaceX’s unwavering commitment to interplanetary exploration, the realization of Earth-to-Earth rocket travel appears to be looming closer on the horizon. The impending inaugural journey to Mars in the early 2020s serves as a testament to the progress made in advancing space travel technologies. The successful execution of interplanetary missions could serve as a stepping stone towards unlocking the potential of rapid global transportation utilizing Starship.
However, the transition from blueprint to a world where humans traverse the globe on the most powerful rocket ever built entails overcoming significant challenges. These formidable hurdles span the realms of engineering, economics, and politics, demanding comprehensive solutions and collaborative efforts.
Starship’s safety
Engineering-wise, the design and development of a robust and safe transportation system that can sustain frequent Earth-to-Earth rocket flights is a paramount undertaking. Innovative engineering solutions must be devised to ensure passenger comfort, minimize environmental impact, and uphold stringent safety standards.
The economic viability of such an ambitious endeavor also warrants careful consideration. The costs associated with constructing and operating a fleet of Starships capable of serving global travel demand must be carefully assessed. Balancing affordability and accessibility while maintaining the exceptional performance and reliability expected from this revolutionary mode of transportation poses a significant economic challenge.

In addition to the technical and financial aspects, the advent of Earth-to-Earth rocket travel entails navigating a complex political landscape. As the concept garners attention and progress accelerates, regulatory frameworks must be established to govern the safe operation of rocket flights, ensure international cooperation, and address airspace regulations. Collaboration among governments, aerospace agencies, and industry stakeholders is crucial to establish comprehensive policies and agreements that foster the growth of this transformative form of travel.
While the vision of Earth-to-Earth rocket travel propelled by SpaceX’s Starship is tantalizing, it is important to approach its realization with cautious optimism. The journey towards a world where humans crisscross the planet on rockets of unprecedented power demands meticulous planning, iterative refinement, and comprehensive testing. The safety, security, and well-being of passengers must remain at the forefront of every decision.
To achieve a safety rating equivalent to traditional airliners, Starship must strive for an exceptionally low mortality rate, aiming for just one death for every 60 million passengers—an achievement the aviation industry successfully reached in 2017. In contrast, the spaceflight industry’s track record currently stands at one death for every 31 astronauts, given the unfortunate loss of 18 lives out of the 564 individuals who have ventured into space.
Efforts to enhance safety measures in space travel are underway, with each crewed mission serving as a stepping stone towards improved safety standards. Nonetheless, significant progress is still required to instill the level of confidence necessary for governments to authorize SpaceX to transport passengers at mind-boggling speeds of 27,000 km/h around the world.
Cost effectiveness
In addition to ensuring safety, Starship must also prioritize cost-effectiveness if it wishes to compete with the commercial airline industry. Renowned airlines such as United, Delta, and American heavily rely on international flights as a substantial revenue source. For SpaceX to make substantial headway in the market, they must strategically position Starship’s ticket prices to be significantly more affordable than traditional air travel.
If SpaceX manages to lower the ticket prices for Starship rides to an attractive level, they could potentially disrupt not only the traditional airline industry but also the logistics sector. Imagine the possibilities if cargo could be transported 25 times faster than airliners—the logistics industry stands to reap immense benefits from such a groundbreaking capability. However, for SpaceX to truly challenge the commercial airline market, they must master the art of rocket reusability. By perfecting the reusability aspect of Starship, SpaceX can significantly drive down operational costs, making their services more economically viable and appealing to a broader consumer base.
The average price for an economy ticket from New York to Shanghai stands at approximately $550, reflecting the affordability that commercial air travel has achieved. In contrast, SpaceX’s Starship, as envisioned by Elon Musk, is projected to accommodate a similar passenger capacity to the Airbus A380, with around 850 individuals on board. Assuming a comparable ticket price, each Starship flight could generate approximately $467,000 in revenue. However, it’s crucial to consider that at this price point, SpaceX would face significant challenges in generating profit once the costs of fueling and launching a rocket of such magnitude are taken into account.

This financial predicament highlights the utmost importance of reusability in the space industry. Currently, SpaceX’s Falcon 9, while considerably cheaper to manufacture than an A380 at around $37 million, has a reusability rate of only 75%. Moreover, the Falcon 9 necessitates extensive and costly refurbishments between flights, ultimately being retired after approximately 10 missions.
To put this in perspective, conventional aircraft such as the Airbus A380 boast an operational lifespan of around 27 years, completing roughly 35,000 flights before retirement. If airplanes were discarded after only a few flights, the commercial air travel industry would not be sustainable, underscoring the significance of reusability in maximizing cost efficiency and minimizing waste.
Unlike the Falcon 9, Starship is designed to be fully reusable and able to endure hundreds of flights before any refurbishment is needed. However, when considering a flight route like New York to Shanghai, the ticket price for a Starship journey would need to be strategically positioned between the affordability of economy class and the premium offering of business class in order for SpaceX to achieve a profit margin that sustains its operations and investment in rocket technology.
Government approval
While addressing the technical and financial aspects is crucial, the journey towards establishing Earth-to-Earth rocket travel is not without formidable challenges, one of the most significant being securing government approval. Gaining global consensus and cooperation from various regulatory bodies is a complex and intricate process, given the multifaceted nature and inherent risks involved. To address concerns regarding public safety and mitigate noise disturbance, SpaceX’s initial approach involves launching and landing Starship at sea, safeguarding populations from potential falling rockets and reducing sound disruptions near heavily populated areas.
However, this strategic choice poses another hurdle for Starship’s potential as a passenger transport vehicle, as it limits the destinations to major coastal cities. Traditional airliners would continue to cater to regional flights, leaving Starship to focus on serving high-demand routes between large coastal metropolitan areas. While this may restrict the reach of Starship in terms of accessibility, it presents an opportunity for SpaceX to collaborate with established airlines and create complementary transportation networks that optimize both regional and long-haul travel.
Another aspect that invites scrutiny is the intense acceleration experienced by passengers during launch and landing. The acceleration forces involved in rocket travel are considerably higher than those encountered in commercial airliners. Addressing this concern is vital to ensure passenger comfort and safety during the journey. SpaceX will need to implement innovative engineering solutions, such as advanced seat designs and effective restraints, to mitigate the effects of acceleration and provide a pleasant travel experience for passengers.
Elon Musk, in his discussions on Starship’s potential as an Earth-to-Earth transport system, acknowledged that the G-forces experienced during the journey would be comparable to those encountered on a roller coaster, typically ranging from 2 to 3 G’s. This particular characteristic of rocket travel may limit its suitability for certain segments of the population, including the elderly, pregnant women, and individuals with heart conditions, who may prefer the affordability and comfort offered by traditional airliners.
While the concept of rockets replacing airliners may currently seem like an ambitious and seemingly impossible dream, it is worth reflecting on history’s lessons. Similar skepticism and doubts surrounded the early days of aviation, where many regarded the idea of manned flight as implausible. However, through persistent innovation and technological advancements, airplanes eventually revolutionized global transportation and became an integral part of our lives.
To gain perspective on our current position in the aviation timeline, it is instructive to consider the state of affairs during the nascent stages of aviation. In the early 20th century, airplanes were predominantly constructed in people’s garages, bearing little resemblance to the advanced and sophisticated aircraft of today. These early aircraft were experimental in nature, often characterized by modest designs and limited capabilities, as the pioneers of flight sought to unlock the true potential of aviation.

In the early stages of aviation, the government recognized the potential of airplanes beyond mere recreational use and identified their suitability for delivering mail across different regions of the country. In an effort to foster innovation, the government initiated contracts accompanied by prize money, challenging inventors and aviation enthusiasts to construct aircraft that could surpass records in terms of speed, altitude, and range.
The future
As airplane technology advanced, significant strides were made in enhancing safety measures, refining engine capabilities, and increasing the size of aircraft, thereby enabling them to accommodate larger volumes of mail for efficient delivery. This progression paved the way for further exploration and exploitation of the possibilities offered by airplanes.
Subsequently, a realization dawned upon individuals that airplanes could serve a purpose beyond mail delivery — they could transport people. This marked the birth of the airline industry, a paradigm shift that forever transformed the landscape of aviation. During the turbulent years of the first and second World Wars, the demand for advanced aircraft reached unprecedented heights, prompting rapid developments in aircraft technology. Notably, 1943 witnessed the introduction of the first jet-powered aircraft, a groundbreaking achievement that revolutionized the capabilities and performance of airplanes.
Fast-forwarding to the present, the year 2022 stands as a testament to the remarkable progress achieved in aviation. Air travel has evolved into one of the safest modes of transportation, thanks to continuous advancements in technology and stringent safety regulations. Modern airplanes are capable of covering vast distances, with some models achieving a range of 9,000 miles, while concurrently accommodating a substantial number of passengers, often reaching as high as 850 individuals per flight. This astounding progress is a testament to humanity’s unwavering commitment to pushing the boundaries of exploration and transportation.












Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!