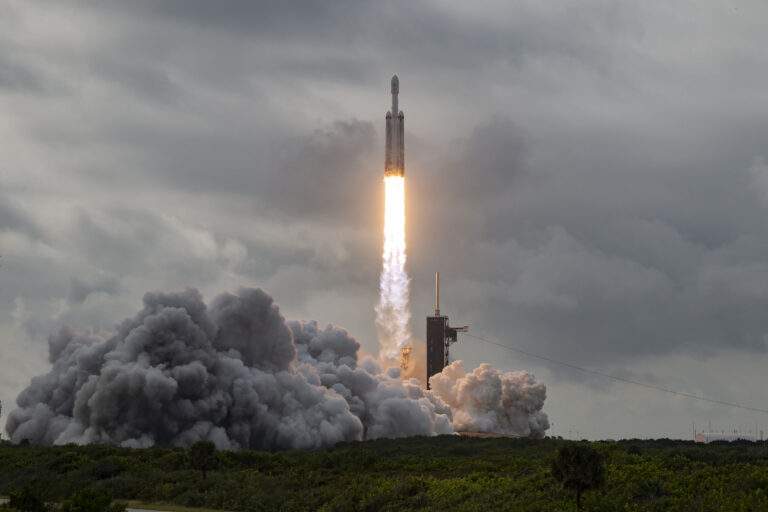
In 2013, SpaceX announced that they were going to try landing their Falcon 9 rocket back on Earth using its own engines. To add to the complexity of this idea, they were going to try landing on a floating droneship in the middle of the ocean.
Something like this had never been done before and at the time, it seemed like an impossible goal. But if it was successful, it would be a massive step forward for rocket reusability. So, SpaceX began experimenting with various test vehicles to learn how to land a rocket. After a couple of years and many explosions, SpaceX finally made the impossible, possible.
Falcon 9 reuse
5 years on from that historic first landing, the iconic sight of a Falcon 9 landing has become routine. With so many launches nowadays, SpaceX have perfected this incredible feat of engineering and saved themselves a lot of money. Each time a Falcon 9 is reflown, they save on the cost of building a brand new booster.

In just the last five years, this has saved SpaceX over 1.4 billion dollars. To this day, SpaceX is the only company that has landed and reused an orbital rocket booster. But now they are focusing their efforts on Starship, the next evolution of crazy space ideas.
Those of us that have followed the Starship program have been treated to some incredible spectacles. The recent SN8 test flight was one of the craziest things SpaceX have ever done. But it showed that their ambitious plans for Starship are more realistic than most of us thought. After all of the crazy things SpaceX have done over the last five years, it seemed like things couldn’t get any crazier. Until this. On Twitter, Elon casually announced a new plan to land the Super Heavy booster.
Catching rockets out of the air
But the plan isn’t to “land” Super Heavy at all. Instead, SpaceX wants to catch it out of the air as it makes its final approach over the launch mount. Although this sounds like another crazy Elon idea, SpaceX aren’t the only company to consider catching rockets out of the sky.
Rocketlab is planning on catching their Electron rocket using parachutes and a helicopter. Back in the 60’s, NASA considered catching the enormous Saturn V first stage using a helicopter with rotor blades over 100 meters long. But let’s not talk about that today. In comparison, SpaceX’s idea sounds a little less crazy.

Why catch instead of land?
So we have established how SpaceX are going to catch the Super Heavy booster. But in order to know why, we need to understand the overall goal of Starship. Starship consists of two stages: the booster stage called ‘Super Heavy’ and the 2nd stage which is just called Starship.
Super Heavy lifts the 2nd stage out of the thickest parts of the atmosphere and Starship does the rest of the work to get into orbit. After separating, Super Heavy comes back down to land, just like the Falcon 9. For Starship, the aim is to travel to the Moon and Mars. In order to achieve this, SpaceX will use a fleet of Starships to refuel in space.
On top of this, SpaceX also wants to use Starship for Earth to Earth passenger travel. This means Starship will need to perform multiple flights a day with a turnaround time on par with airliners. Not only does it have to have a quick turnaround time, it has to be strong and reliable enough to deal with multiple flights a day.
The original plan for Super Heavy was to land directly onto the launch mount, making it instantly ready for its next flight. Although this would have many benefits, it would require a level of precision much greater than SpaceX have shown with their Falcon 9 landings.
So, SpaceX moved to the idea of landing Super Heavy on a landing pad and using a giant crane to lift it onto the launch mount. This would require at least six extremely large landing legs with enough shock absorption to handle the landing. But this is where the problems come in. Perhaps one of the areas SpaceX has learned the most with their Falcon 9 landings is the landing legs.
For the Falcon 9 landings, the booster needs to be transported back to a refurbishment hangar where many components are replaced and inspected. One of the most critical parts in their refurbishment process is the landing legs. All of this takes an enormous amount of time which isn’t an option for Super Heavy. Removing the legs from the design completely, would not only simplify the turnaround time, but it would also save an incredible amount of weight.

Every kilogram of mass saved, will allow the rocket to carry heavier payloads into orbit. With 6 legs on the Super Heavy, the overall mass of the landing gear would be around 10% of the entire booster upon landing. But without any legs, SpaceX’s only option is to catch the booster. This will still require a great amount of precision since it since the booster will need to hit its marks almost perfectly.
Super Heavy advantage over the Falcon 9
One of the big advantages Super Heavy has over the Falcon 9 is its ability to hover. Even with just one engine firing, the Falcon 9 is too powerful to hover so it has to perform a suicide burn. This involves firing its engine at just the right time, bringing the vertical velocity to zero the moment it touches the ground.
If it started this burn too early, the rocket would slow all the way down and start to climb before it reached the ground. If it started the burn too late, it wouldn’t slow down in time and it would crash into the ground. Since Super Heavy has more engines than the Falcon 9, it can reduce its thrust-to-weight ratio to 1. This will allow it to hover over the pad and give it extra time to adjust its course.
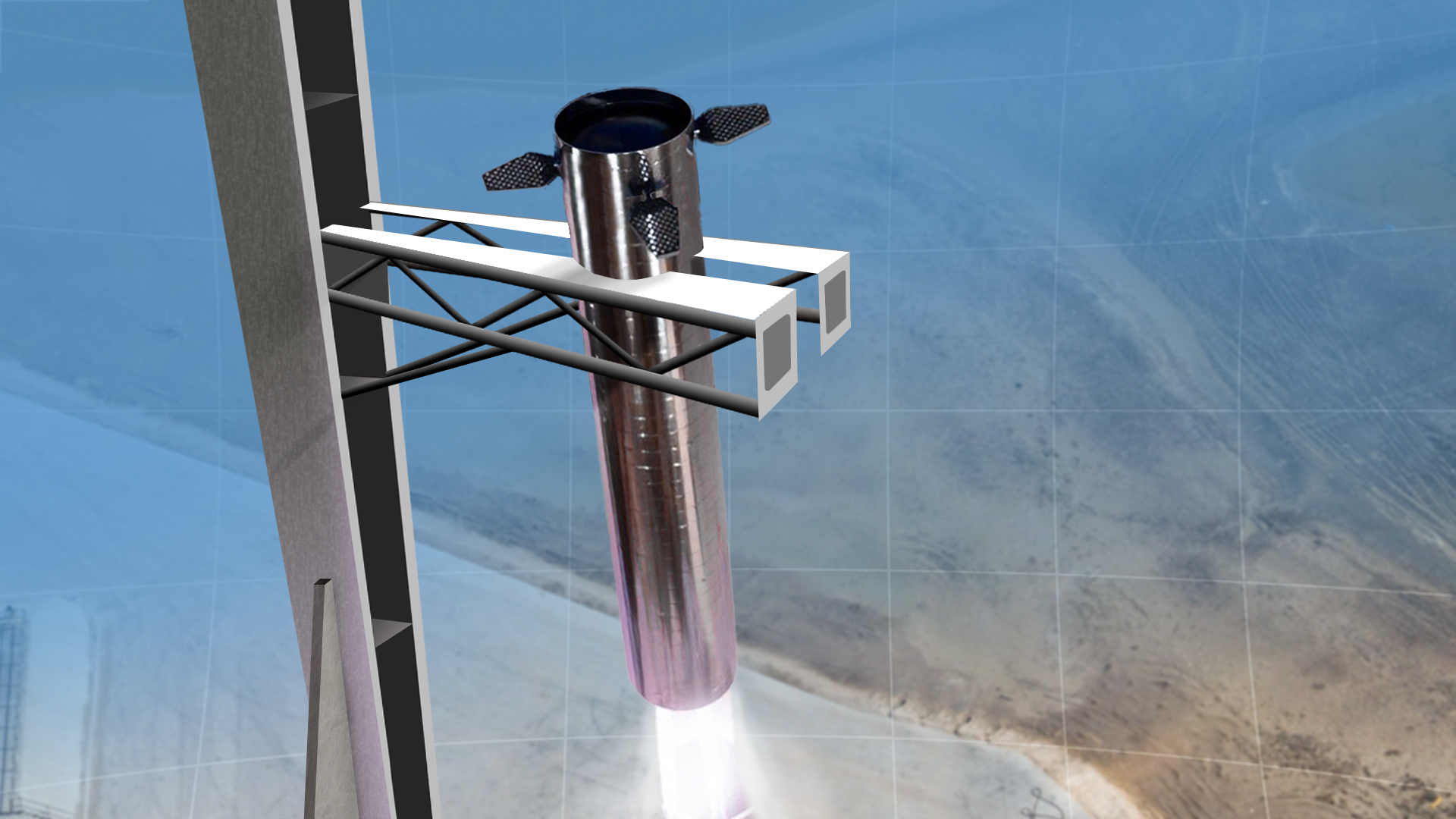
SpaceX will try to catch the booster on its final approach using a giant arm attached to the launch tower. As Super Heavy comes into land, it will thread the needle between these catching arms until they retract inwards and lock into place.
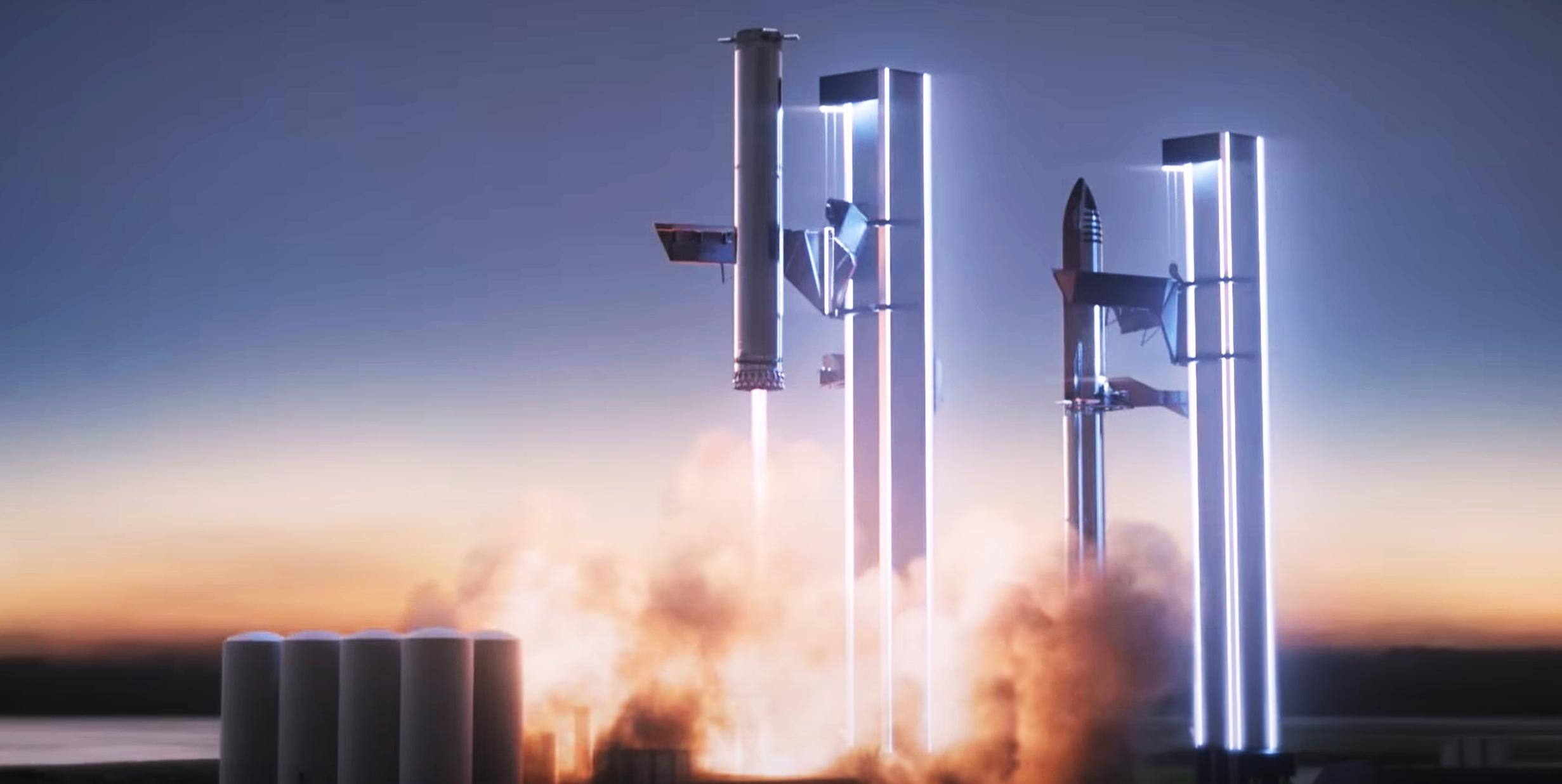

One of the key points about this idea is that the catcher will hook onto the grid fins which will need to take the load of the entire booster. At first, this seems like an incredible amount of force to exert on the grid fins. But since they are designed to handle a large amount of drag upon reentry, they are already extremely strong in this direction. The Super Heavy gridfins are also not designed to fold out (unlike the Falcon 9) and they will always be sticking out for the full duration of a mission. This means it can be made extra strong in this direction.
Maybe something like this pic.twitter.com/PUBLdaewt8
— Elon Musk (@elonmusk) January 20, 2022
Despite this unique method of landing, it will still require shock absorption to handle the last bit of energy and bring the booster to a standstill. Normally this shock absorption would be handled by the landing legs.
On the Falcon 9, the landing legs consist of telescopic tubes that are filled with compressed helium. As the legs fold in on themselves, the compressed gas acts as a shock absorber. The main thing here is that the shock absorption will be built into the catcher and not the rocket.
This will reduce the amount of stress on the rocket, taking away any need for major refurbishment. SpaceX will likely use a similar system of air suspension but on a much larger scale.
Taking all of this away from the rocket and transferring it onto the landing arm will allow Super Heavy to be as light as possible, without putting too much stress on the rocket. But weight saving is only part of the puzzle. The real benefit here is the ability to rapidly relaunch the booster.
Faster reusability
If it can be immediately lowered onto the launch mount after a landing, the booster can be secured, detanked and inspected for its next flight. After all, the detanking process is especially important for Starship since it will still contain excess methane after it lands. Methane isn’t allowed to be vented into the atmosphere so SpaceX plans to pump the leftovers back into the tank farm for it to be recondensed and used for the next flight.
So although we might have to wait a few more years for SpaceX to attempt this crazy idea, it’s inspiring to see them taking on these incredible engineering challenges. When SpaceX landed their first booster 5 years ago, it made us rethink what is possible and advanced the world of spaceflight massively. No matter what happens, it’s clear that we are witnessing history being made.












Thank you very much for sharing, I learned a lot from your article. Very cool. Thanks.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!